020 – Magnetization
Introduction to:
Magnetization by means of permanent magnet, ferromagnetism, magnetic needle, compass, Earth’s magnetic field, north and south pole
Material:
- Permanent magnet (e.g. bar magnet, as strong as possible)
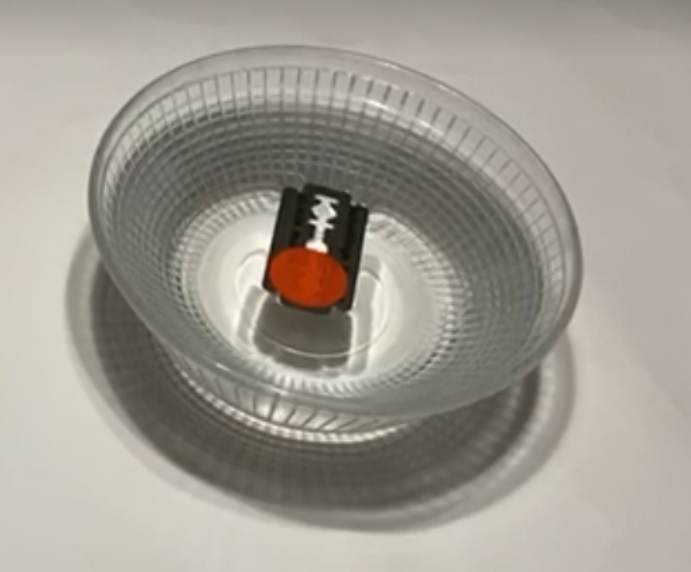
- Razor blade with a marking (e.g. red dot)
- Bowl with water
Material (alternative):
- needle (e.g. pin) (1)
- cork / styrofoam / wooden discs (2)
- Permanent magnet (e.g. bar magnet, as strong as possible)
- Bowl with water
Construction and implementation:
- Run one pole of the permanent magnet over the razor blade several times in the same direction, preferably over the top and the bottom.
- Carefully place the razor blade on the surface of the water.
- It always returns to the north-south direction, even if you turn it.
Explanation:
- By running the permanent magnet over the razor blade, the magnetic domains in the iron align.
- This turns the razor blade itself into a magnet.
Didactic potential:
- A nice brain teaser is to figure out the orientation of the razor blade. Do not forget that there is a magnetic south pole at the geographic north pole of the Earth.
- The experiment consolidates the model of the elementary magnets in iron.
Tips:
- The magnetisation can be reversed by strong vibration/shock
- Caution: Move the permanent magnet far away from the bowl to prevent interference with the magnetic field of the Earth
Tips for alternative material:
- Before attaching the needle to the cork disc, test whether it is really magnetized (for example, hold it against a needle that has not yet been magnetized).
- Modelling clay works well for attaching the needle, glue is also possible