197 – Multiple Reflection
Introduction to:
- Reflection
- Transmission
- Refraction
Material:
- Safety note: Risk of damage to the retina, therefore use LASERs with low radiation power. Never work without LASER safety glasses!)
- Mirror (with a glass plate as thick as possible, thickness at least 5 mm)
- Projection surface (e.g. white sheet of paper)
Instructions:
- Light up the mirror with the laser pointer at an angle of about 30°-45°. Observe the safety advice!
- Capture the glow on a projection screen perpendicular to it.
Observation:
- We can see at least three points of light on the projection surface, the second from above is the brightest.
Explication:
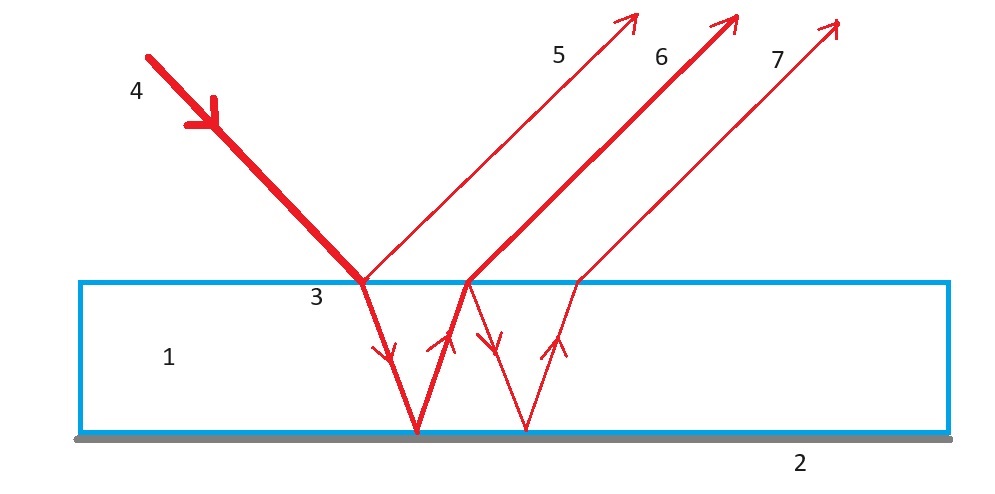
Schematic drawing:
- 1 glass plate of the mirror
- 2 mirrored underside of the glass plate
- 3 Top of the glass plate
- 4 incident light beam (LASER)
- 5 Beam reflected directly on the glass plate
- 6 beam reflected at the mirror and refracted twice
- 7 beam reflected twice at the mirror
- The top light point 5 is created by the reflection at the top of the glass plate of the mirror. The brightest light point 6 is caused by reflection on the mirrored underside of the glass plate. The light is refracted twice, when entering and exiting the glass. The third light point 7 is created by a single reflection from the inside at the top of the glass plate of the mirror and a renewed reflection at the mirrored underside.
- Any other visible points of light are caused by multiple reflections on the mirror and on the glass surface.